
The Wyandotte and Olathe Pregnancy Clinics provide a variety of services at no cost, so you can make an informed and empowered choice for your unplanned pregnancy!
Pregnancy Tests
Have you missed your period? Are you experiencing pregnancy symptoms? Perhaps you’ve already taken a pregnancy test at home, but want a second opinion.
We provide pregnancy tests at no cost so you can be certain you are pregnant. Results are 99% accurate and 100% confidential!
Ultrasounds
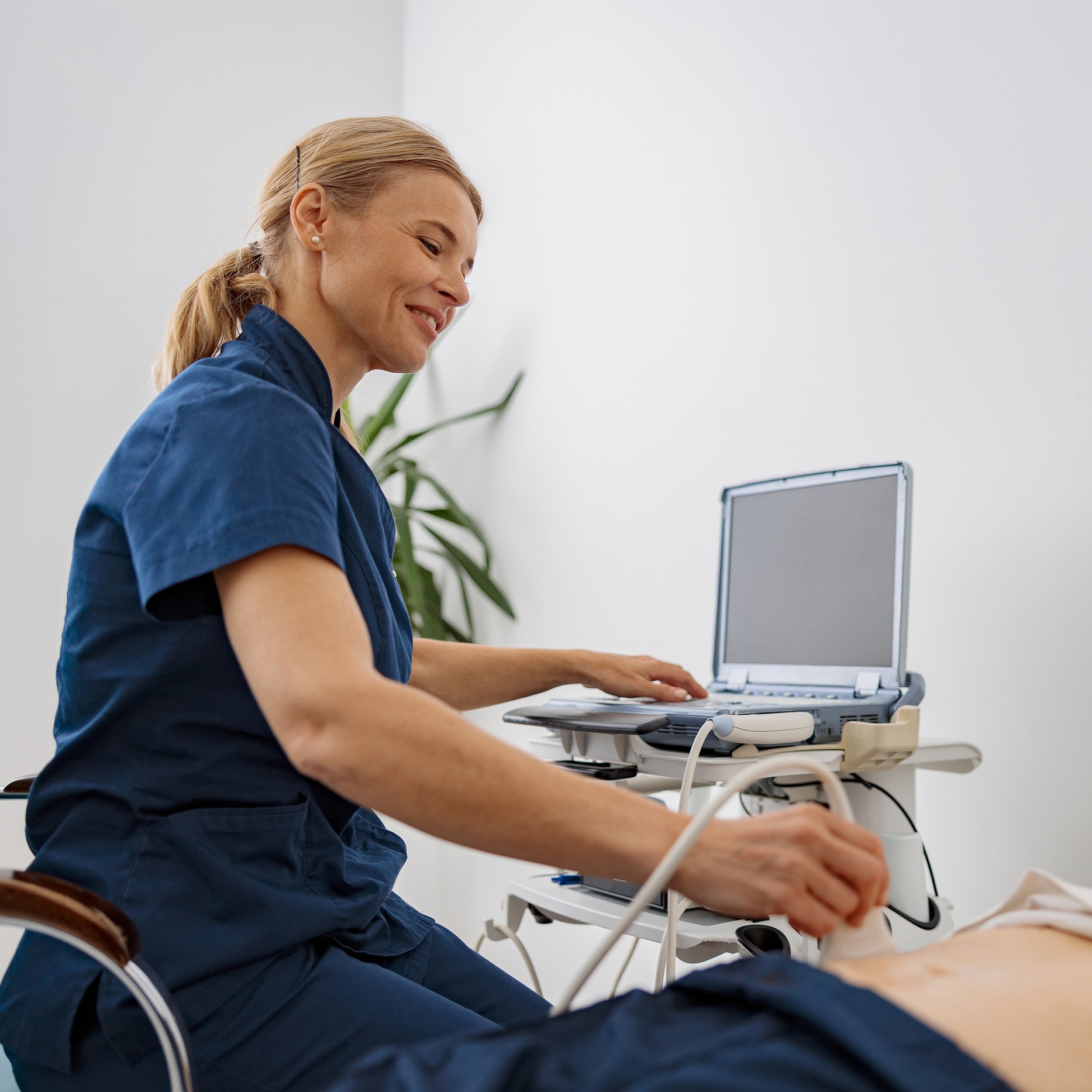
Ultrasounds provide vital information about your pregnancy! They confirm how far along you are in your pregnancy and whether or not the pregnancy is developing properly inside the uterus. Having this information will inform your abortion* options going forward!

STIs
It’s crucial to get tested for STIs regularly, as many don’t have obvious symptoms. Additionally, STIs can increase your risk of developing a post-abortive infection.
We provide STI testing and treatment at NO COST, so you can protect your health.


Unplanned Pregnancy Services in Kansas
Don’t wait to get the care you deserve! Call us at (913) 287-8287, text us at (913) 735-3262, or schedule your appointment online today.
